Dependency Injection | Code Quality Assurance

Have you every wondered, what’s the difference between writing code and good quality code that scales easily even after many years, which has in fact gone through various developers throughout it’s life cycle and is still working fine and can be further scaled. You know when you come across such type of code that a good quality code. There are many factors that differentiate a simple code and a good quality code.
One of the factors that determine the quality of the code is dependency injection. How well are two classes talking to each other within a program, how well are their objects talking to one another. According to Wikipedia, dependency injection is defined as a technique whereby one object (or static method) supplies the dependencies of another object. Now, what does it actually mean? Within this blog post we are going to answer this question and learn the following:
- What is dependency injection
- How do we apply dependency injection on two classes?
- Advantages of dependency injection
What is dependency injection?
In layman terms, suppose you have to buy a car. You look at the various models of the car, their engine horsepower, facilities, seat spacing and all the basic requirements. You finally decide to buy a car and bring it home. Now, the next day you won’t change the engine because you wish to have a higher horse power or would break open the car because you want more leg space. No, right. You would state the requirements beforehand and then buy a car according to the requirements. That is what dependency injection is all about.
You state the requirements in the constructor by making the objects talk to one another instead of passing values from one constructor to another. This is what dependency injection is all about.
How do we apply dependency injection on two classes?
Let’s look at a simple example to add two numbers. Consider the following piece of code:
Every thing seems correct, right! But it’s not. There are a number of problems associated with this code and are going to break it down and use the dependency injection to solve the challenges. Following are the problems with this piece of code:
- This is just calculating the sum of first and second number. Now, what if we want to calculate the sum of three numbers we have to play with the parameter value which leads to fragile code and can be broken easily.
- Secondly, we see that the Sum method is validating first value and second value and then returning the sum which leads to a lot of responsibility on the class.
- Thirdly, negations are used in the if conditions which makes it difficult for the reader to read the code.
We would be tacking these three challenges and write clean quality code using dependency injection.
In order to tackle the challenge, we need to change the approach used to calculate the sum of numbers from a procedural approach to object oriented approach. For that, let’s consider the following UML diagram.
[caption id="attachment_220" align="alignnone" width="583"]
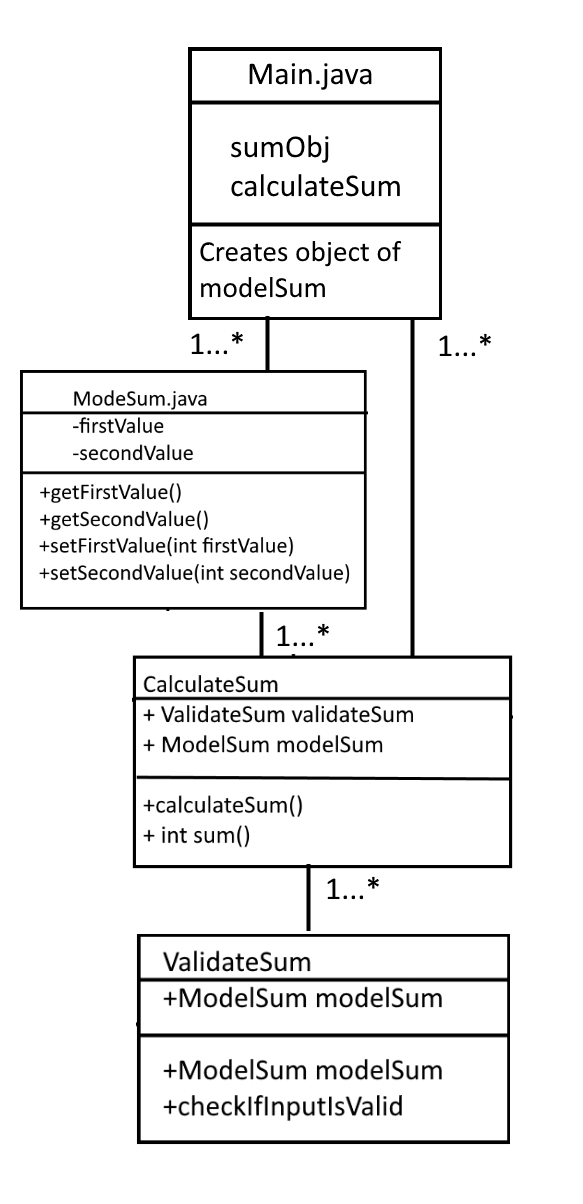 UML diagram related to sum of two numbers[/caption]
UML diagram related to sum of two numbers[/caption]
Using the above UML diagram, we can now clearly see how the request would flow from main and how the objects would talk to one another. The first challenge we had was to remove the dependency from the constructor and we did that by encapsulating the firstValue and secondValue in a different class called ModelSum.java which contains the getter and setter for the firstValue and secondValue.
Now instead of the class depending on first and second value, it’s now dependent on encapsulated class and we can now pass the object of these classes in the constructor. This is the entire process of dependency injection. We are now making the class depend on the object of the encapsulated class instead of the passed values. Thus, we have solved the problem of passing parameter values by passing the object as a parameter.
Model sum code is shown below. Corresponding calculate sum class that calls the model sum is shown below: The next problem was that the single class was validating the values and returning the sum. We solved the problem by creating a separate validated class that validates the input values from the modelsum. Code for validateSum is shown below: Next problem we saw with the code was to that negations was used in if conditions. We solved it by simple reversing the condition as shown in validateSum.java code above.
That’s all for dependency injection. To summarize, we understood what dependency injection was. We saw various challenges with an existing code and used dependency injection on a code that used functional programming and converted the code to object oriented way and applied dependency injection it.
Within the next tutorial we would look at test driven development. How it would fit our existing sum code and what all we can do with test driven development.

 Never miss a story from us, subscribe to our newsletter
Never miss a story from us, subscribe to our newsletter